Breaking Down the Biomechanics of Effective Swimming Techniques
The art of swimming has transcended time and cultures, evolving from a survival skill to a popular sport and recreational activity. In this article, we delve into the fascinating world of swimming biomechanics to understand what makes an effective technique. We explore the physics that govern movement in water, dissect popular strokes, and outline training strategies that can help swimmers optimize their performance.
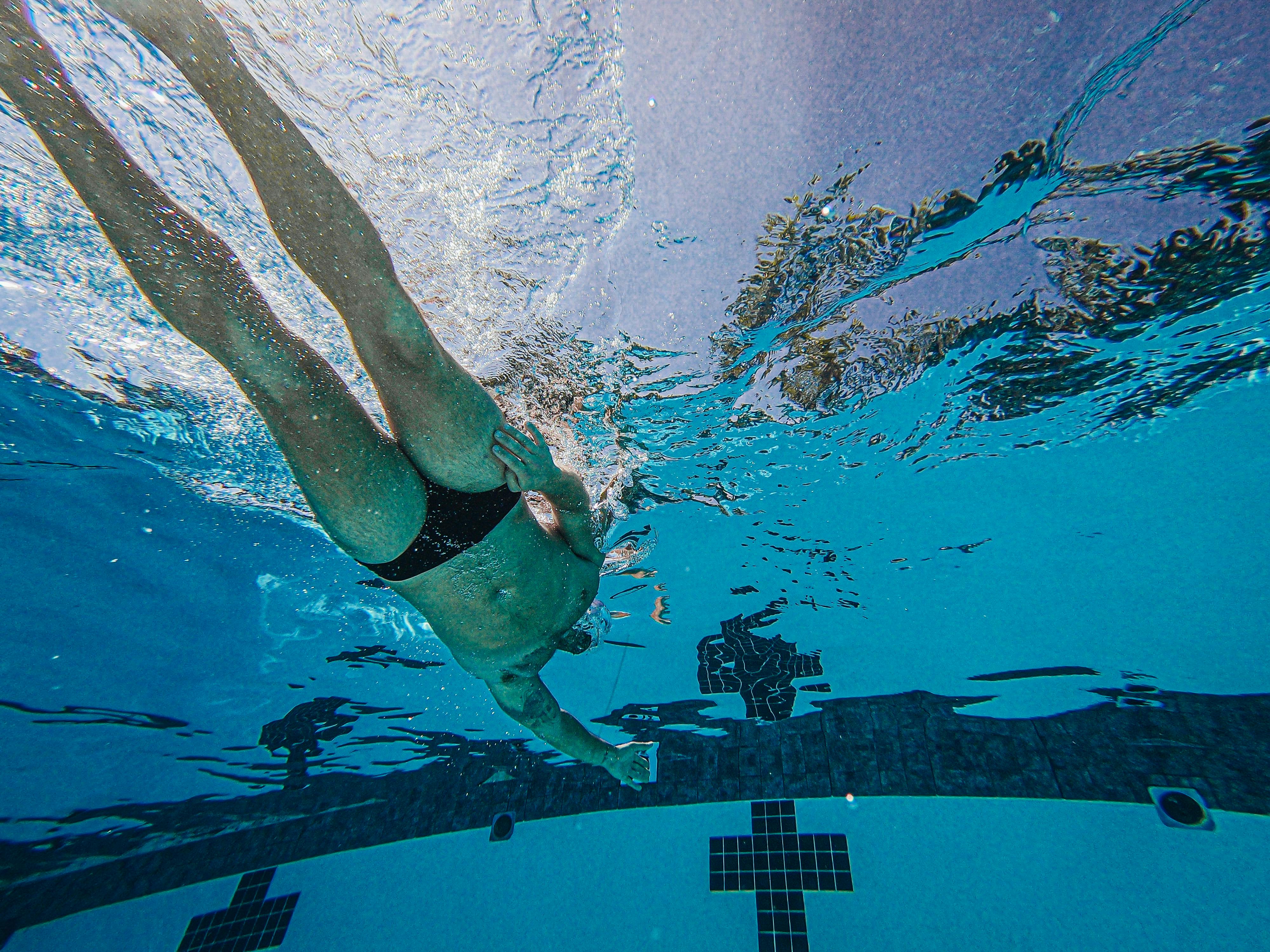

The Physics of Swimming: Understanding Drag and Propulsion
Swimming is essentially a balancing act between drag and propulsion. Drag refers to the resistance a swimmer encounters while moving in water, while propulsion is the force that drives the swimmer forward. The key to efficient swimming lies in minimizing drag and maximizing propulsion.
Dissecting Popular Swimming Strokes
Not all swimming strokes are created equal. Each stroke—be it freestyle, breaststroke, backstroke, or butterfly—has its unique biomechanical principles, advantages, and challenges.
Freestyle: The Speed Demon
Freestyle, or front crawl, is known for its speed and efficiency. This stroke focuses on continuous arm movements and an alternating breathing pattern, demanding a balance of strength, endurance, and technique.
Breaststroke: The Power Player
Breaststroke is a complex yet powerful stroke. It involves simultaneous movements of the arms and legs in a whip-like motion, requiring precise coordination and timing.
Backstroke: The Upside-Down Marvel
Backstroke, the only stroke performed on the back, offers unique challenges and opportunities. The swimmer must maintain a streamlined body position while moving backward, highlighting the importance of spatial awareness and body control.
Butterfly: The Energy Guzzler
Butterfly, often considered the most physically demanding stroke, combines symmetrical arm movements with a dolphin kick. This stroke requires exceptional strength, flexibility, and endurance.
Training Strategies for Optimal Performance
By understanding the biomechanics of swimming, coaches and athletes can design training programs that enhance stroke efficiency, power, and endurance. Here are some strategies that can help:
Strength and Conditioning
Targeted strength and conditioning exercises can improve a swimmer’s power and endurance. Core stability exercises, for instance, can enhance body alignment and control, resulting in reduced drag and improved propulsion.
Technique Drills
Technique drills focus on specific aspects of a stroke, helping swimmers refine their movements, improve coordination, and increase efficiency.
Flexibility Training
Flexibility is critical in swimming, especially for strokes like the butterfly and breaststroke. Regular stretching can improve joint mobility, reduce the risk of injury, and enhance stroke efficiency.
In conclusion, the biomechanics of swimming is a complex yet fascinating field that offers valuable insights for athletes and coaches. By understanding the principles that govern movement in water, swimmers can refine their technique, optimize their training, and ultimately, enhance their performance.